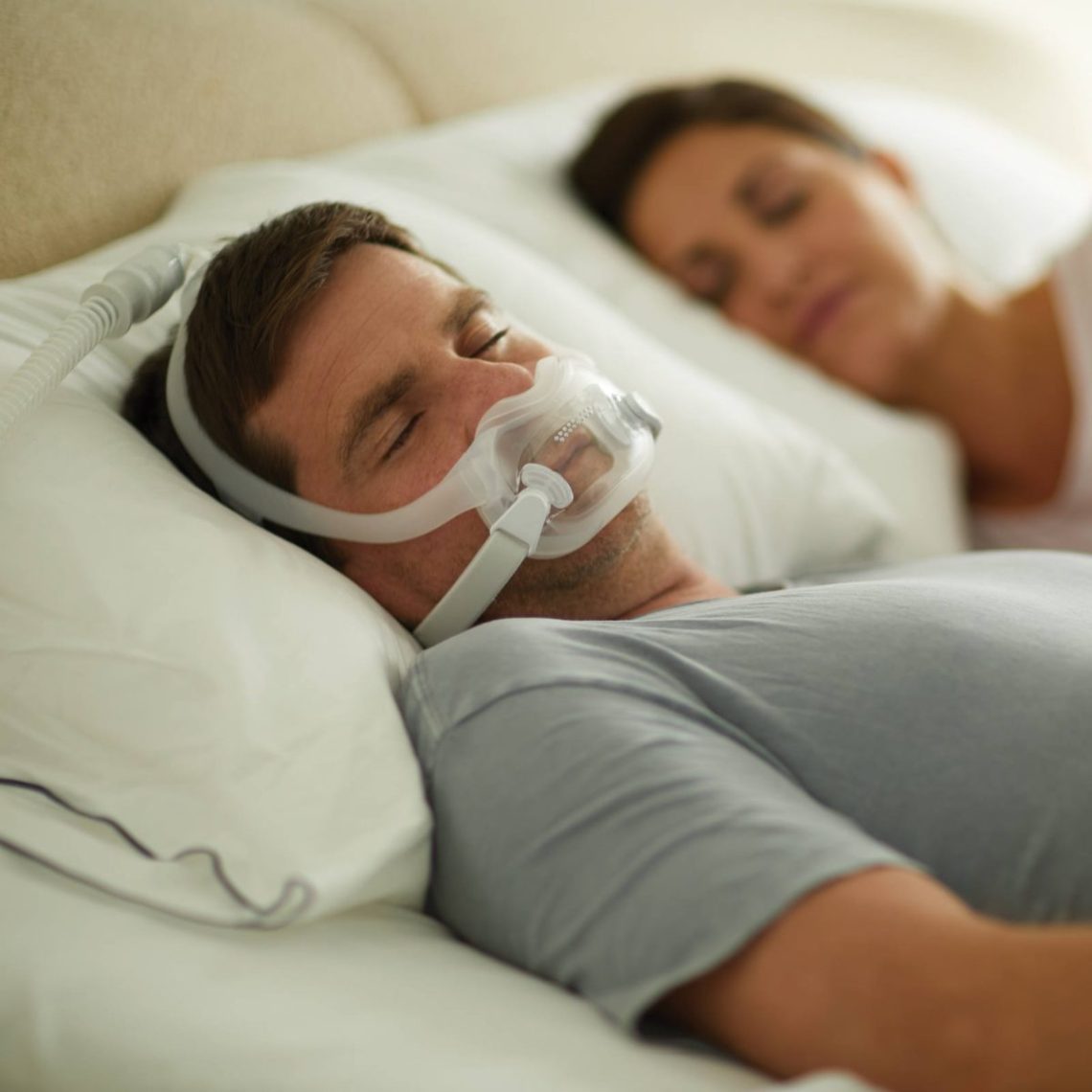
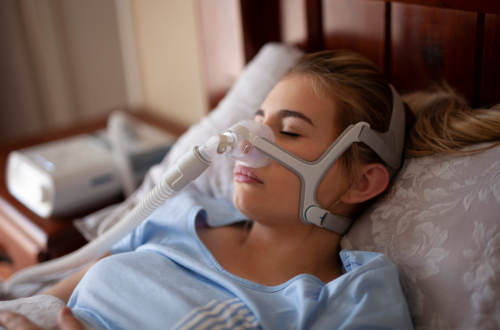
Sleep is meant to be a time of restoration — a break from the noise of the day and a reset for both the body and mind. But for those living with sleep apnea, the quiet of the night is anything but restful.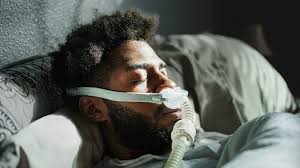
Sleep apnea is a common yet serious disorder that causes breathing to repeatedly stop and start during sleep. If left untreated, it can impact more than just your rest — it can raise your risk for heart disease, diabetes, memory loss, and more.
In this post, we’ll break down what sleep apnea is, how to recognize the signs, and what you can do to manage it effectively.
—
🧠 What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a condition where your breathing is interrupted during sleep, often multiple times per hour. These interruptions can last anywhere from a few seconds to over a minute — and they jolt your body out of deep sleep, even if you don’t fully wake up.
There are three types:
– Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common form, caused by a physical blockage of the airway (usually the soft tissue in the back of the throat).
– Central Sleep Apnea: The brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
– Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A combination of both obstructive and central types.
—
⚠️ Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Many people with sleep apnea don’t even know they have it. Often, it’s a partner who notices the signs.
Common symptoms include:
– Loud, chronic snoring
– Gasping, choking, or pauses in breathing during sleep
– Waking up with a dry mouth or headache
– Feeling exhausted during the day, no matter how long you slept
– Difficulty concentrating, irritability, or mood swings
– Waking up frequently at night
If you identify with several of these symptoms, it’s worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
—
🔍 What Causes Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea can affect anyone, but certain factors increase your risk:
– Excess weight or obesity
– Narrow airway or enlarged tonsils
– Aging (especially over 40)
– Smoking or alcohol use
– Nasal congestion or sinus issues
– Family history of sleep apnea
—
🛠️ How Is Sleep Apnea Diagnosed?
Your doctor may recommend a sleep study (polysomnography), either at a sleep clinic or through an at-home device. These tests monitor your breathing, heart rate, oxygen levels, and sleep stages.
Diagnosis usually involves identifying how many times you stop breathing per hour (your apnea-hypopnea index, or AHI). Higher scores indicate more severe apnea.
—
💡 Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
The good news? Sleep apnea is highly treatable. Options include:
1. Lifestyle Changes
– Lose weight if overweight
– Avoid alcohol and sedatives before bed
– Sleep on your side instead of your back
– Treat nasal allergies
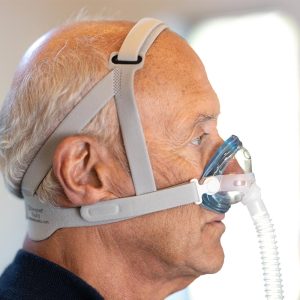
2. CPAP Therapy (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure)
– A CPAP machine keeps your airway open with gentle air pressure through a mask.
– It’s the most common and effective treatment for moderate to severe OSA.
3. Oral Appliances
– Custom-fitted dental devices reposition your jaw to keep the airway open.
4. Surgery (in severe cases)
– Removal of tissue, tonsils, or correcting structural issues may be recommended when other treatments fail.
 —
—
🌙 Final Thoughts
Sleep apnea is more than just snoring — it’s a serious health issue that can quietly wear down your body, mind, and quality of life.
If you or someone you love shows signs of sleep apnea, take it seriously. Talk to your doctor, schedule a sleep study, and explore treatment options that can restore your sleep and protect your health.
Need help building better sleep habits while you seek a diagnosis?
Download our free 7-Day Sleep Reset Plan — a gentle, natural way to support deeper sleep starting tonight.
Breathe easier. Sleep deeper. Live better.